Best Manufacturer & Suppliers of Transformer Monitoring System

Ready to Optimize Your Transformer Performance?
Why Choose Our Transformer Monitoring System?
Our Transformer Monitoring System is engineered to provide real-time data, enabling proactive maintenance and preventing costly downtime. With advanced sensors and analytics, you gain a comprehensive overview of transformer health, identifying potential issues before they escalate.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Stay ahead with 24/7 surveillance.
- Predictive Maintenance: Reduce unexpected failures and extend transformer life.
- Cost-Efficiency: Minimize maintenance costs and operational disruptions.
Ready to transform your power management?
Get Started with Our Transformer Monitoring System Today!
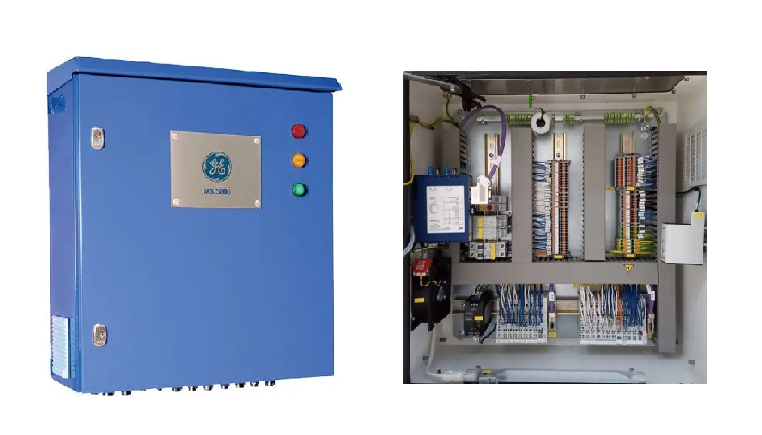
Key Features of Our Transformer Monitoring System
- Continuous supervision of the whole transformer, integrating data from available sensors
- Modular: essential through to comprehensive coverage of transformer failure modes
- All information available at a glance, even across several substation transformers
- An “Expert System” to help you assess and manage your costly assets
- Optimum operation efficiency with reduced life-cycle cost
- Web server HMI, no need for software to access the data analysis
- Integration with GE’s Perception software for centralised information and leveraging of fleet data**
- Easy inter-operability of the transformer with the Smart Grid / Digital Substation
Our TMS is packed with features that make it an indispensable tool for modern power management:
Applications of Transformer Monitoring System
- Suitable for most transformer types and ratings, independent of manufacturer
- Applicable to new and existing transformers
- Used in power generation, transmission and distribution
- Special solutions for HVDC applications
- Ideal for industries with process interruption risks
Boost your grid’s performance now.
Contact Us for More Information
Areas of Use On line Smart Breather
Refinery, Fertilizer Units, Pharmaceuticals, Agricultural Collages, Biotechnology Laboratories, Private and Government Analytical Testing Laboratories, Collages- Botany, Applied Physics, Civil, Mechanical, Chemistry, Applied Chemistry, Food and Nutrition,LPG Plants, Pollution Control Laboratories, Defence, Atomic Energy, Space, Paint Industry,Fine Chemicals Industry, Oil Manufacturers, Dairy, R & D Laboratories. Environmental Analysis, Solvent Analysis, Fatty Methyl Esters, Flavours, Essence, Wax, Nuclear Power Plants, Heavy Water Plants.
Our Valued Clients